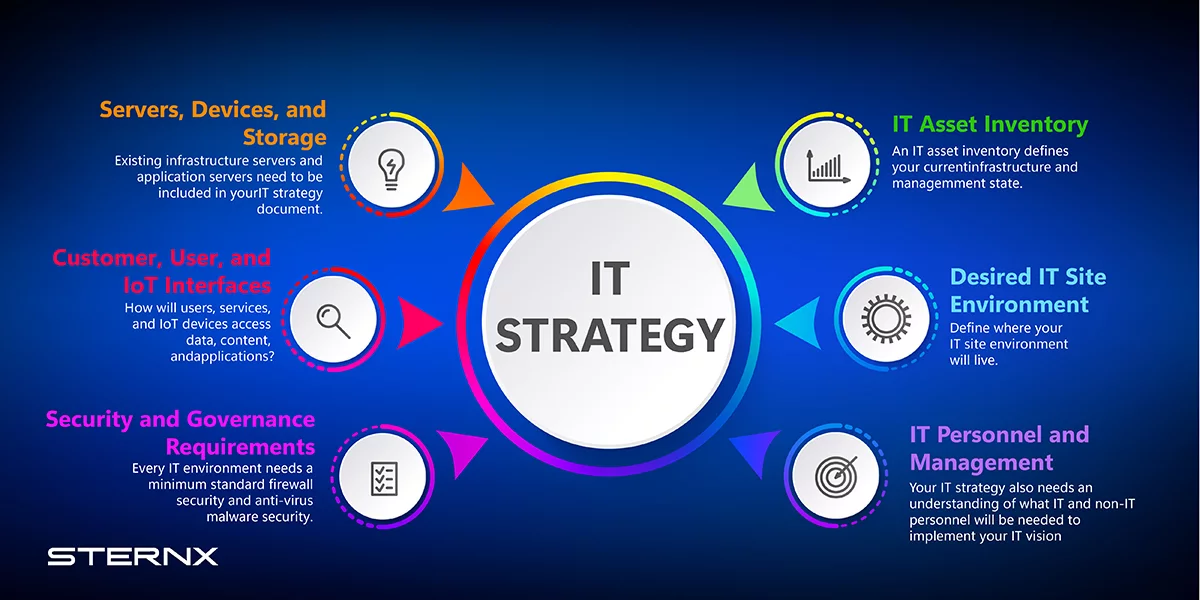
What is an IT Strategy? An information technology (IT) strategy outlines a company’s high-level plan for using technology to achieve business objectives. It details how technology should support and enable the company’s goals. An effective IT strategy aligns with the company’s overall business strategy. It should outline how to leverage technology like software, hardware, networks, and services to enhance productivity, efficiency, decision-making, and growth.
Table of Contents
ToggleImportance Of An IT Strategy
Having a clear, well-thought-out IT strategy is crucial for companies in today’s digital world. Consider these key reasons why an IT strategy matters:
Supports Business Goals:
It keeps technology efforts focused on core business goals instead of letting tech advancements lead the strategy. This intentional alignment ensures technology fuels overarching objectives.
Optimizes Resources:
A strategy guides smart investment in tech, tools, and software. This prevents wasted spending on redundant, unnecessary, or outdated solutions. Companies stretch their budgets further with an IT roadmap.
Enhances Security:
Cyber Threats pose one of the largest risks today, making security vital. An IT strategy prioritizes protection through steps like hacker detection, access controls, encryption, and robust backup systems.
Boosts Efficiency:
The right technology makes it easier for employees to do their jobs, eliminates redundant efforts, and streamlines communication. An IT strategy maps out how to leverage tech for maximum productivity.
Enables Scaling:
Growth comes with growing technology needs. A scalable IT strategy provides a plan for expanding systems, supports, tools, and networks as the company adds customers, products, services, or locations.

Strategies For Preventing Cyber Threats
With cyberattacks more sophisticated than ever, an IT strategy must address security. Steps for guarding against phishing, ransomware, data breaches, and other digital threats include:
- Installing firewalls, anti-malware software, and intrusion detection across networks
- Setting up VPNs and requiring multi-factor authentication for remote access
- Enforcing strong password policies and access controls
- Training employees on responsible online behavior and phishing detection
- Performing penetration testing to find and patch vulnerabilities
- Backing up data regularly with both local and cloud-based storage
- Creating an incident response plan for handling breaches
Continuous evaluation ensures measures evolve alongside emerging risks. Keeping software updated offers protection through the latest security patches as well.
IT Solutions to Guard Against Phishing and Ransomware
Specific IT safeguards necessary for combating phishing schemes and ransomware attacks include:
Phishing Defenses
- Email filters to analyze incoming messages and quarantine risky emails
- Employee awareness training for identifying fraudulent links/attachments
- Secure email gateways to block access to suspicious domains
- DMARC authentication and spam blacklists to reject spoofed emails
Ransomware Defenses
- Limiting access rights to minimize ability to infect systems
- Safely backing up data for fast recovery after an attack
- Using emerging tech like blockchain for secure, unalterable backups
- Installing and updating antivirus software across all endpoints
- Setting software to block known ransomware file types and activity
Keeping emergency response protocols in place for suspected infections can further mitigate damage. Applying patches right when available also reduces exploitable vulnerabilities.

Ongoing Assessment of the IT Strategy
An IT strategy is not a one-and-done document. Regular evaluation and updating ensures it remains aligned with evolving business objectives and accounts for new technological advancements.
Aim to review the formal IT strategy annually, with interim check-ins every six months. During assessment, consider aspects like:
- Changes to overall business goals and direction
- Performance of current tech investments
- Emergence of innovative new solutions
- Shifts in processes or operations
- Growth of teams, workspace, or customer base
- New cybersecurity threats in the landscape
- Compliance with updated regulations
- Feedback from leadership and end users
This analysis will reveal where strategy adjustments are beneficial. It might highlight needs for replacing legacy systems, adopting automation tools, or expanding network capabilities. Reviews also verify that existing elements like data protection measures still adequately serve the organization.
Any revisions made to the IT strategy should happen collaboratively. Include feedback from departmental leaders, essential personnel, and the C-suite. This ensures buy-in to support effective adoption of technology initiatives company-wide.
Key Takeaways
- An IT strategy is essential for harnessing the best of technology according to specific business goals. It steers innovation in the right direction.
- The complexity of today’s cyber risk landscape makes security a top IT priority. Phishing, ransomware and other threats require layered protection.
- Regular check-ins ensure the existing IT strategy remains tightly aligned to evolving organizational needs. Technology progresses quickly, so assessments at least every 6 months keeps the strategy effective as a decision-making guidepost.
With a well-designed and frequently evaluated IT roadmap, IT solution companies make the most of their tech investments. They position themselves for resilience when threats arise and nimbleness when opportunities emerge. An up-to-date strategy grants leader’s confidence in technology’s ability to propel operations now and in the future.
Developing and adhering to an intentional IT strategy aligns tech efforts with an organization’s overarching mission. It guides smart investments, optimizes resources, boosts efficiency, and enables scaling. But in today’s threat landscape, cybersecurity sits chief among technology priorities. A strategy detailing robust protections, incident response, and continuous improvement offers assurance. By planning proactively around emerging risks like phishing and ransomware, companies secure smooth operations.